Questions
- What does it mean for a RLHF model to forget context?
- How are the reward models combined to generate RLHF feedback? Is it in the form of just 2 scalar values or is there a more complex weightage going on
- How did PPO go and why did it manage to bring up the performance?
- How does the loss function for the reward models work intuitively? Why does the m(r) term at the end of the eqn help to guide the model to make value judgements.
-
Trained 3 diff models - 7b , 13b and 70b with a base model and a chat model
-
Training Stages
- Pre-Training ( but without meta customer data )
- Fine-Tuning ( using SFT data from a variety of vendors )
- RLHF ( using two reward models - one for helpfulness and safety)

-
Model Architecture
- Transformer vanilla architecture
- RMS Norm as a pre-activation
- SwiGLU activation functions
- Encoding is done using Bytepair Encoding and Rotary Positional Embeddings with the implementation of Grouped Query Attention to make computation more effective.
-
Supervised Fine Tuning
- Bootstrapped initial stage with publicly available instruction tuning data. Subsequently augmented with third-party and vendor annotation. Eventually collected ~ 27,540 annotation
-
Human Feedback
- Annotators are given two prompts which are sampled from two different model variants with varied temperature hyper-parameters
- Safety Label : Ranges from 0 safe, 1 safe and 2 safe
- Preference : Participants are asked to rank based on a binary comparison protocol
- Human annotations collected on a weekly basis to allow for annotations to reflect the new weekly model’s data distribution. This helps to keep the reward model on-distribution and to maintain an accurate reward for the model.
- Annotators are given two prompts which are sampled from two different model variants with varied temperature hyper-parameters
-
Reward Modelling
- 2 separate reward models trained - one for helpfulness and one for safety.
- Underlying tension between safety and helpfulness since a model that is super safe might classify a lot of questions as harmful, thus reducing helpfulness
- Reward model is initialised from pretrained chat model checkpoint but they replace final classification head ( that gives the token probs ) with a regression head to output a scalar reward
- Custom binary ranking loss is used to train the reward model with the collected pairwise human preference data converted into a binary ranking label format.
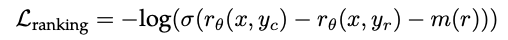
- 2 separate reward models trained - one for helpfulness and one for safety.
-
RLHF :
- Created a total of 5 versions with a new version generated after each update to the reward models - RLHF V1,… RLHF V5
- Mainly used
- Proximal Policy Optimization ( PPO )
- Rejection Sampling Fine Tuning : Sample K outputs from the model and select the best candidate with our reward. They use a re-ranking strategy whereby sample with the highest reward score is the gold standard and all other samples are now re-ranked
- Note : Rejection Sampling was performed only with the largest 70B model with other models being fine-tuned on rejection sampled data from the larger model
-
Multi-Turn Consistency
- RLHF models tend to forget the initial instructions after a few turns of dialogue ( ? What does this even mean )
- Introduction of Ghost Attention ( GAtt ) which introduces an instruction which must be followed throughout the dialogue and measures model ability to follow the instructions
- General Approach was to create a few synthetic constraints to sample from : Hobbies, Language and Public Figure before getting llama-2-Chat to sample from it. Final instruction combines a bunch of prior constraints.
- Generally find that GAtt is constant up to 20 turns