Google Drive is a file sharing service which acts as a competitor to Dropbox
Questions
I came up with the following questions
- How many users
- What is the maximum file size?
- What file types are supported?
- Do we need to implement file encryption?
Here were some additional questions
- What are the most important features?
- Is this a mobile app, web app or both?
Estimations
We estimate that we have
- Approximately 50 million users, with 10 million Daily Active Users (DAU)
- Each user being given ~10GB of space
- Each user uploads around 2 files per day that is around 500kb in size This indicates that we have
- Around 1mb uploaded per user, 10 million * 1 mb = 10 TB of space / day
- Around 10 million * 2 = 20 million uploads per day which translates to roughly 20 / 24 / 3600 ~ 230 queries/second
- This translates to about 460 peak QPS
Design
We want to provide three high level apis
-
UPLOAD : We have a single api for users to be able to upload files to. This should support two types of uploads - simple and resumable uploads. This is because for larger files, we want to use a multipart upload so that in the event of any interruption, we only need to re-upload a small part of the file instead of the entire file.
-
Download : Users should be able to download the file
-
Revisions : This is an API which returns information on the various revisions - users should be able to utilise this in order to download prior versions of the files they have uploaded.
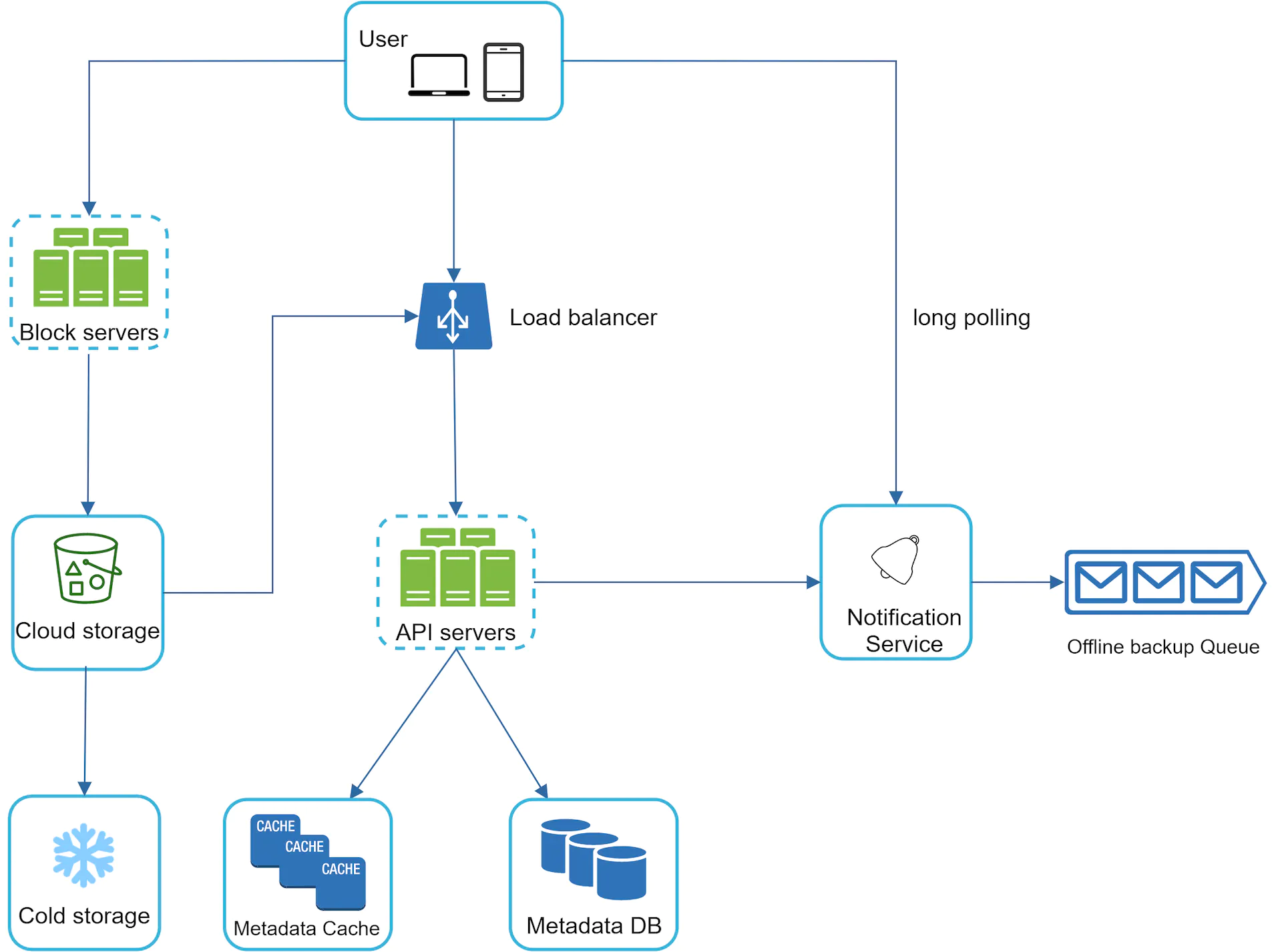
On a high level
-
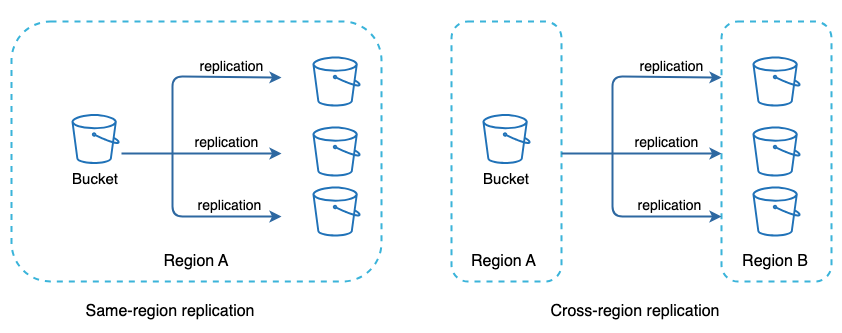
Cloud Storage : We utilise a service like S3 to store our files. This allows us to have files stored in cross and same-region . This guards against potential data loss and ensures availability for users.
-
Cold Storage: We utilise cold storage as a way to reduce costs. For files that are uploaded and then rarely or never accessed, we can use a service like AWS S3 Glacier
-
Metadata DB : This stores information on the user’s files. We offload some of this data into a metadata cache to help reduce db load.
-
Notification Service : We utilise a notification service to help users get notified when there are changes to their files. This helps them to pull the latest changes as they come.
-
Offline backup queue: If a client is offline and cannot pull the latest file changes, the offline backup queue stores the info so changes will be synced when the client is online.
Concepts
Sync Conflicts
When we are syncing file changes across multiple clients, we will end up with a case whereby different clients upload different versions of the same file, causing a conflict. In this case, when there is no automatic way to resolve these differences, we should instead
- notify the user that there has been a merge conflict
- create two separate versions of the file so that users can decide which one to keep
Block Sync
Instead of storing the entire file, we can split our file into blocks - which are each going to be around 4mb each ( dropbox spec ). This can be done using a block server.
Block servers process files passed from clients by splitting a file into blocks, compressing each block, and encrypting them. Instead of uploading the whole file to the storage system, only modified blocks are transferred.
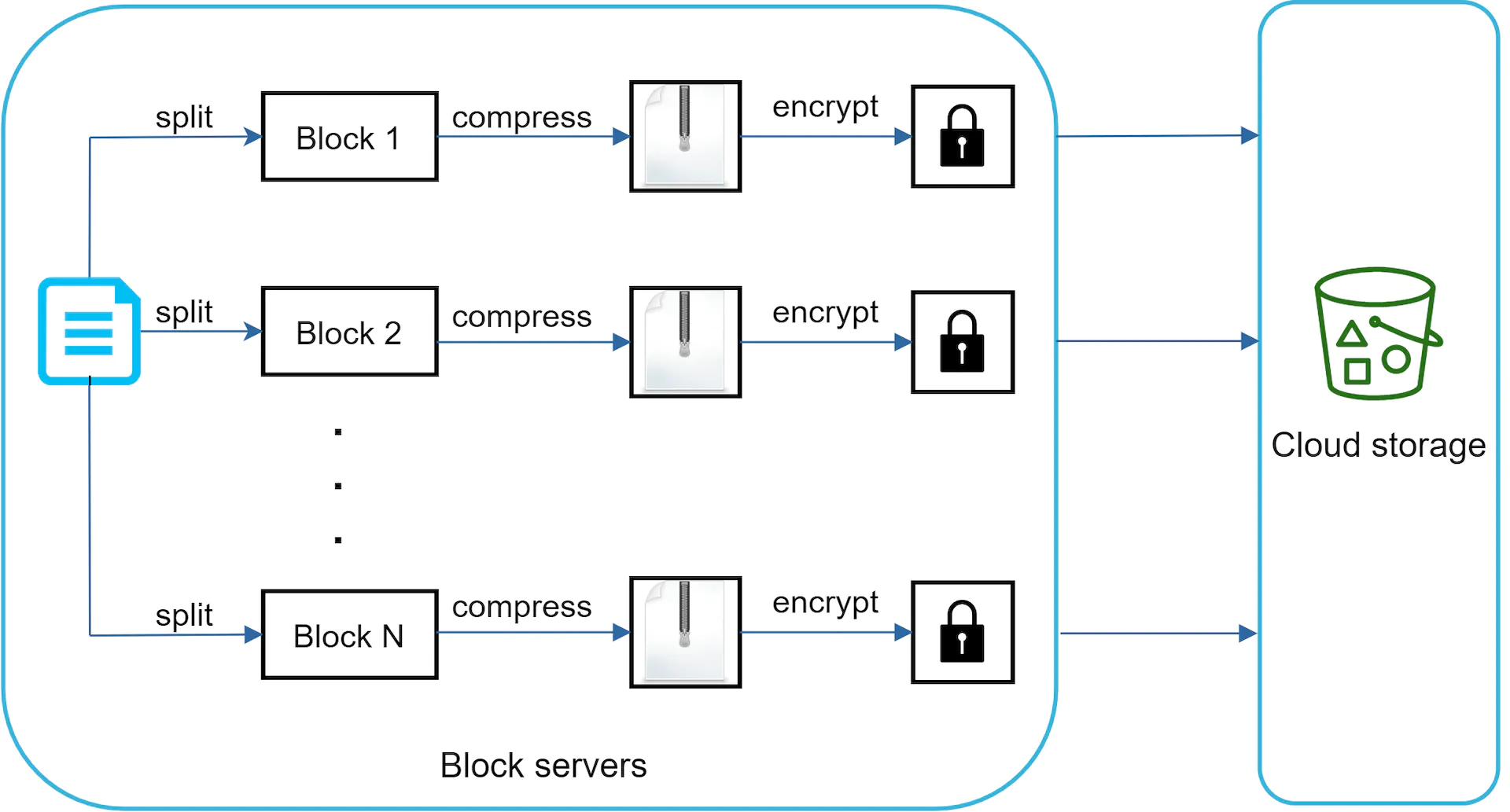
This means that when the file changes, only the blocks that have changed need to be updated. We can potentially save on the update costs
Consistency Requirement
Our system requires strong consistency by default. It is unacceptable for a file to be shown differently by different clients at the same time. The system needs to provide strong consistency for metadata cache and database layers.
Memory caches adopt an eventual consistency model by default, which means different replicas might have different data. To achieve strong consistency, we must ensure the following:
- Data in cache replicas and the master is consistent.
- Invalidate caches on database write to ensure cache and database hold the same value.
Storage Optimization
We can save on storage with the following
-
De-duplicate data blocks. Eliminating redundant blocks at the account level is an easy way to save space. Two blocks are identical if they have the same hash value.
-
Adopt an intelligent data backup strategy. Two optimization strategies can be applied:
-
Set a limit: We can set a limit for the number of versions to store. If the limit is reached, the oldest version will be replaced with the new version.
-
Keep valuable versions only: Some files might be edited frequently. For example, saving every edited version for a heavily modified document could mean the file is saved over 1000 times within a short period. To avoid unnecessary copies, we could limit the number of saved versions. We give more weight to recent versions. Experimentation is helpful to figure out the optimal number of versions to save.
-
-
Moving infrequently used data to cold storage. Cold data is the data that has not been active for months or years. Cold storage like Amazon S3 glacier [11] is much cheaper than S3.