Problem Statement
Consistent Hashing allows us to correctly allocate requests across server by computing a hash
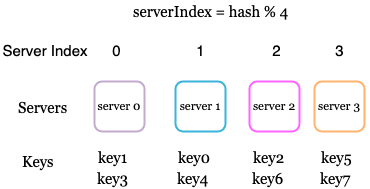
If we simply take the number of servers that we have and use that to calculate the hash
Eg. RequestId = 422 and we have 4 servers
422 % 4 = 2 # Therefore we allocate to the 3rd server
This causes a problem down the line when either the number of servers changes or the data distribution becomes uneven. Imagine if server 3 goes down and we keep directing requests to it, this would cause a lot of problems
Therefore, we can try to fix this issue by performing consistent hashing.
Methodology
Our hash function can be mapped onto a hash space or ring as seen below
There are a few methods that we can utilise this hash function
Using a Hash Server
We assume here that we are using the SHA-1 hashing algorithm
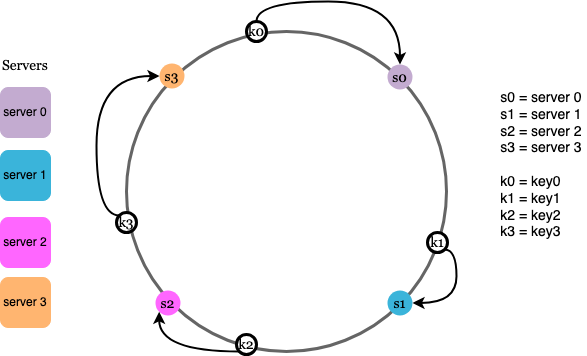
We first compute a hash of our server ip
f(server ip) = hash value
This is mapped onto our hash ring as seen by s0...s3 which represent the computed hashes of the 4 servers that we have. We can then compute which server our key should be on by first computing its hash
f(request id ( or something else we're using ))
and then going clockwise from that value to find the first instance of a server hash that we can find. This means that when a server goes down and we need to remove it’s hash value, only a small fraction of keys require a redistribution - rebalancing is quite easy to implement.
Using Virtual Nodes
However, there are two main problems with the approach above
- The space between each server node might not be uniform -> since we cannot compute a reverse hash of the hash function easily (I.e. the original value to produce a desired hash )
- The distribution of data in the ring component corresponding to the server node might not be uniform
Therefore, we can use virtual nodes - which are arbitrary mappings onto the hash space
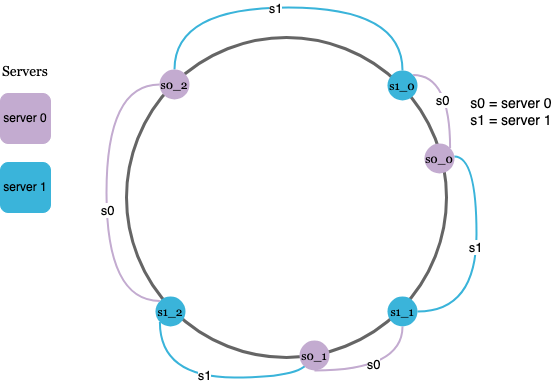
To find which server a key is stored on, we simply go clockwise from the key’s location and find the first virtual node encountered on the ring. In order to find out which server a request key is stored on, we simply go clockwise and find the first virtual node.
As the number of virtual nodes increases, the distribution of keys becomes more balanced. This is because the standard deviation gets smaller with more virtual nodes, leading to balanced data distribution.